Glossary
Ischemia
The restriction of blood supply to a tissue.
—————
Arachnoid Villi
Prolongations of pia-arachnoid that protrude through the meningeal layer of the dura mater. They act as one way valves that move the cerebrospinal fluid from the subarachnoid space to the venous system.
—————
Tentorial Notch
A triangular opening in the cerebellum through which the brainstem extends.
—————
Tight junctions
When cell membranes join together so tightly that they are virtually impermeable to fluid.
—————
Choroid Plexus
An area on the ventricles of the brain where all CSF is produced.
—————
Lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a white blood cell. It is part of the innate immune system.
Image adapted from Wikipedia.
—————
Isotonic Solution
A solution that has esqual osmotic pressure to the cell.
—————
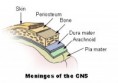
Subarachnoid Space
The space between the arachnoid mater and pia mater which surround the brain.
Image from Wikipedia.
—————
Intraventricular foramina
Channels that connect the brain ventricles.
—————
Ventricular System
A set of structures in the brain continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord. The ventricular system transports cerebrospinal fluid. The ventricular system includes the lateral ventricles, the third ventricle and the fouth ventricle.
—————
Did you know?
Diseases such as meningitis can infect cerebrospinal fluid?